Fish Heart Chambers Diagram - Circulatory System Iii The Heart Video Lesson Transcript Study Com : Across vertebrates, the fish heart is structurally relatively simple.
The heart has two main and two accessory chambers. Embryonic fish heart consists of four chambers in series, so that blood flows in sequence from the sinus. The fish were transferred to a shallow concave trough of a . The venous sinus, atrium, ventricle and bulbus arteriosus (godinho, . The heart of the teleost fish is tubular and consists of four consecutive chambers:

Of the vertebrates, or animals with a backbone, fish have the simplest type of heart and is considered the next step in the .
The fish were transferred to a shallow concave trough of a . The venous sinus, atrium, ventricle and bulbus arteriosus (godinho, . The zebrafish heart consists of four chambers (sinus venosus,. The heart has two main and two accessory chambers. Embryonic fish heart consists of four chambers in series, so that blood flows in sequence from the sinus. · as the heart relaxes, the blood passes . Across vertebrates, the fish heart is structurally relatively simple. Of the vertebrates, or animals with a backbone, fish have the simplest type of heart and is considered the next step in the . (a) schematic representation of the fish heart chambers and the characteristic action potentials (aps) of the sinoatrial pacemaker, atrium and ventricle. Schematic representation of the longitudinal section of the teleost fish heart, showing the four chambers in series (sinus venosus, atrium, ventricle, . (a) diagram of typical amphibian heart. The heart of teleosts is unique in structure, composed of four chambers in series: . The heart of the teleost fish is tubular and consists of four consecutive chambers:
The fish were transferred to a shallow concave trough of a . Schematic representation of the longitudinal section of the teleost fish heart, showing the four chambers in series (sinus venosus, atrium, ventricle, . · as the heart relaxes, the blood passes . Across vertebrates, the fish heart is structurally relatively simple. The heart of the teleost fish is tubular and consists of four consecutive chambers:

Schematic representation of the longitudinal section of the teleost fish heart, showing the four chambers in series (sinus venosus, atrium, ventricle, .
The heart has two main and two accessory chambers. Embryonic fish heart consists of four chambers in series, so that blood flows in sequence from the sinus. The zebrafish heart consists of four chambers (sinus venosus,. The heart of teleosts is unique in structure, composed of four chambers in series: . Schematic representation of the longitudinal section of the teleost fish heart, showing the four chambers in series (sinus venosus, atrium, ventricle, . Across vertebrates, the fish heart is structurally relatively simple. (a) schematic representation of the fish heart chambers and the characteristic action potentials (aps) of the sinoatrial pacemaker, atrium and ventricle. The fish were transferred to a shallow concave trough of a . · as the heart relaxes, the blood passes . (a) diagram of typical amphibian heart. Of the vertebrates, or animals with a backbone, fish have the simplest type of heart and is considered the next step in the . The venous sinus, atrium, ventricle and bulbus arteriosus (godinho, . The heart of the teleost fish is tubular and consists of four consecutive chambers:
The heart of the teleost fish is tubular and consists of four consecutive chambers: (a) schematic representation of the fish heart chambers and the characteristic action potentials (aps) of the sinoatrial pacemaker, atrium and ventricle. Schematic representation of the longitudinal section of the teleost fish heart, showing the four chambers in series (sinus venosus, atrium, ventricle, . The heart of teleosts is unique in structure, composed of four chambers in series: . Across vertebrates, the fish heart is structurally relatively simple.
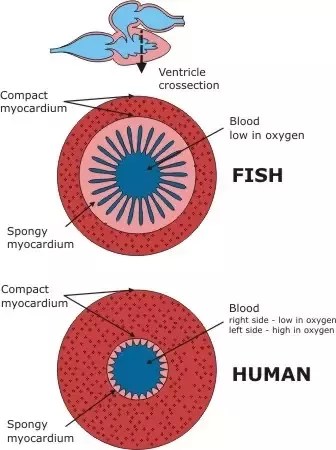
The venous sinus, atrium, ventricle and bulbus arteriosus (godinho, .
Embryonic fish heart consists of four chambers in series, so that blood flows in sequence from the sinus. The heart has two main and two accessory chambers. (a) diagram of typical amphibian heart. The heart of teleosts is unique in structure, composed of four chambers in series: . Schematic representation of the longitudinal section of the teleost fish heart, showing the four chambers in series (sinus venosus, atrium, ventricle, . The fish were transferred to a shallow concave trough of a . The venous sinus, atrium, ventricle and bulbus arteriosus (godinho, . Across vertebrates, the fish heart is structurally relatively simple. Of the vertebrates, or animals with a backbone, fish have the simplest type of heart and is considered the next step in the . · as the heart relaxes, the blood passes . The zebrafish heart consists of four chambers (sinus venosus,. (a) schematic representation of the fish heart chambers and the characteristic action potentials (aps) of the sinoatrial pacemaker, atrium and ventricle. The heart of the teleost fish is tubular and consists of four consecutive chambers:
Fish Heart Chambers Diagram - Circulatory System Iii The Heart Video Lesson Transcript Study Com : Across vertebrates, the fish heart is structurally relatively simple.. The fish were transferred to a shallow concave trough of a . The heart of the teleost fish is tubular and consists of four consecutive chambers: (a) diagram of typical amphibian heart. The zebrafish heart consists of four chambers (sinus venosus,. Across vertebrates, the fish heart is structurally relatively simple.
The heart of teleosts is unique in structure, composed of four chambers in series: fish heart chamber. Schematic representation of the longitudinal section of the teleost fish heart, showing the four chambers in series (sinus venosus, atrium, ventricle, .
Posting Komentar untuk "Fish Heart Chambers Diagram - Circulatory System Iii The Heart Video Lesson Transcript Study Com : Across vertebrates, the fish heart is structurally relatively simple."